by Dick Hall-Sizemore
For all those readers who complain that Northern Virginia gets screwed by state funding formulas, Dwight Yancey of Cardinal News has provided an eye-opening rejoinder. Many rural counties have been hit disproportionately hard by the new calculations for the local composite index used to determine the local share of the costs of basic aid for schools.
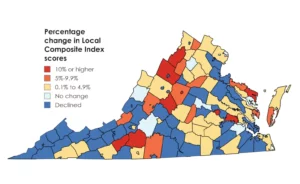
The main driver in these increases has been significant increases in the total value of real estate in those counties. Many of them have become havens for folks leaving urban areas for the rural countryside, either for their primary or secondary homes. In Franklin County, burgeoning property values around Smith Mountain Lake have driven up the county’s total real property values 39 percent over the past two years, although almost half the students live in poverty. In Nelson County, the situation is much the same with properties in Wintergreen and spillover from Albemarle County driving up the county’s total property values. In Charles City County, where 64 percent of the students live in official poverty, folks buying up riverfront property have driven up the total property values by 24 percent.
The result of these changes is that the state now considers Charles City County as having a greater ability to pay for its schools that Northern Virginia localities, including Loudoun County, the wealthiest locality in the state and one of the wealthiest in the nation. In fact, 22 localities are rated as having a greater ability to pay than Loudoun and most of them are rural.
Yancey provides nice maps to illustrate his analysis.
At some point, the state—governor and legislature—will have to quit delaying and tackle the hard job of revising how the state funds local schools.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.